Polar See-saw on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
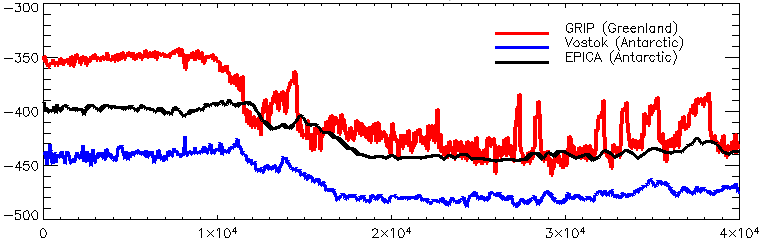 The polar see-saw (also: bipolar seesaw) is the phenomenon that temperature changes in the northern and southern hemispheres may be out of phase. The hypothesis states that large changes, for example when the glaciers are intensely growing or depleting, in the formation of ocean bottom water in both poles take a long time to exert their effect in the other hemisphere. Estimates of the period of delay vary; one typical estimate is 1,500 years. This is usually studied in the context of
The polar see-saw (also: bipolar seesaw) is the phenomenon that temperature changes in the northern and southern hemispheres may be out of phase. The hypothesis states that large changes, for example when the glaciers are intensely growing or depleting, in the formation of ocean bottom water in both poles take a long time to exert their effect in the other hemisphere. Estimates of the period of delay vary; one typical estimate is 1,500 years. This is usually studied in the context of
 The polar see-saw (also: bipolar seesaw) is the phenomenon that temperature changes in the northern and southern hemispheres may be out of phase. The hypothesis states that large changes, for example when the glaciers are intensely growing or depleting, in the formation of ocean bottom water in both poles take a long time to exert their effect in the other hemisphere. Estimates of the period of delay vary; one typical estimate is 1,500 years. This is usually studied in the context of
The polar see-saw (also: bipolar seesaw) is the phenomenon that temperature changes in the northern and southern hemispheres may be out of phase. The hypothesis states that large changes, for example when the glaciers are intensely growing or depleting, in the formation of ocean bottom water in both poles take a long time to exert their effect in the other hemisphere. Estimates of the period of delay vary; one typical estimate is 1,500 years. This is usually studied in the context of ice cores
An ice core is a core sample that is typically removed from an ice sheet or a high mountain glacier. Since the ice forms from the incremental buildup of annual layers of snow, lower layers are older than upper ones, and an ice core contains ic ...
taken from Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest cont ...
and Greenland
Greenland ( kl, Kalaallit Nunaat, ; da, Grønland, ) is an island country in North America that is part of the Kingdom of Denmark. It is located between the Arctic and Atlantic oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Greenland i ...
.
See also
* Polar amplification *Climate of the Arctic
The climate of the Arctic is characterized by long, cold winters and short, cool summers. There is a large amount of variability in climate across the Arctic, but all regions experience extremes of solar radiation in both summer and winter. Som ...
*Climate of Antarctica
The climate of Antarctica is the coldest on Earth. The continent is also extremely dry (it is a desert), averaging of precipitation per year. Snow rarely melts on most parts of the continent, and, after being compressed, becomes the glacier ic ...
References
* * * Meteorological phenomena Environment of Antarctica Climate and weather statistics {{Climate-stub